Participation of a Forensic Medical Expert in Inquests
I.E.Loban*, I.V.Kurganova*
* Leningrad Regional Bureau of Forensic Medical Examination,
Saint Petersburg, Russia
|
In accordance with the Russian Federation legislation, experts in the field of forensic medicine are widely recruited to participate in different inquests besides examinations. These are crime scene inspection, exhumations, corpse identifications, examination of living persons, interrogations, inquiry experiments, procurement of comparative samples, etc. Many of them have not been researched thoroughly before. To define their position among other forms and means of applying forensic medical knowledge in investigation, selective information has statistically been analyzed concerning expert participation in inquests.
The information was accumulated in 14 of all 21 District Departments of Leningrad Regional (LR) Bureau of Forensic Medical Examinations during the past three years - 1998-2000 (table 1). Medical examiners took part all in all in 3351 inquests during these three years. Among them, crime scene inspection, i.e. examinations of accident or crime places and corpse on discovery constituted the majority - 2302 (68.7 per cent of all inquests). The forensic medical inspection of corpses in respect to total forensic autopsies was 10.6%, in respect to the violent death - 19.1%, and in respect to all homicides - 77.8%. Diagram 1 demonstrates the correlation between the percentage of crime scene inspection and the total number corpse forensic medical examinations.
The proportion of all the other inquests where forensic medical specialists participated amounted to 31.3% (Diagram 2). Among them corpse identifications numbered 445 cases which made up 13.3% of all inquests with participation of medical examiners and average 23,6/1000 autopsies (Diagram 3); inquiry experiments and checks of evidence on a crime scene - 155 (4.6% and 7.0/1000 autopsies); procurement of comparative samples - 138 (4.1%); interrogation of medical examiners - 134 (4.0% and 5.9/1000 autopsies); inspection and collecting of injury objects (weapons), vehicles etc. - 99 (3.0%, 3.7/1000 autopsies and 3.3 for total living persons examinations); interrogations of suspected and defendant - 32 (1.0% of all inquests); examination of living persons - 23 (0.7%); searching (0.3%), exhumations - 11 (0.3% and 0.6/1000 autopsies).
There were investigating agencies that initiated inquests in those cases (69.4 per cent), lawyers (2.5 per cent) and medical examiners themselves (28.1 per cent). In most cases, inquiries were undertaken in the course of primary forensic medical examinations (52.3 per cent), and less often, as additional (21.8 per cent) and repeated (17.7 per cent) examinations or in court (8.2 per cent).
The statistical findings characterize the important aspect of medical examiner's work and may be used in forensic medical service administration.
Table 1. The participation of medical examiners in inquests (selective statistical analyses of expert practice in Leningrad Region, 1998-2000)
INQUESTS |
YEAR |
TOTAL N % |
per 1.000 autopsies |
per 1.000 examina- tions of living persons |
|
||
1998 n % |
1999 n % |
2000 n % |
|||||
Crime scene inspection |
707 72,7 |
813 71,8 |
782 62,9 |
2302 68,7 |
121,9 |
_ |
|
Corpse identification |
82 8,4 |
135 11,9 |
228 8,3 |
445 13,3 |
23,6 |
_ |
|
Inquiry experiments |
52 5,3 |
48 4,3 |
55 4,4 |
155 4,6 |
7,0 |
0,8 |
|
Procurement of comparative samples |
32 3,3 |
39 3,4 |
67 5,5 |
138 4,1 |
5,8 |
1,0 |
|
Interrogation of medical examiners |
38 3,9 |
41 3,6 |
55 4,4 |
134 4,0 |
5,9 |
2,4 |
|
Inspection of injury objects (weapons), transport etc. |
31 3,2 |
29 2,6 |
39 3,1 |
99 3,0 |
3,7 |
3,3 |
|
Interrogations of suspected and defendants |
13 1,3 |
11 1,0 |
8 0,6 |
32 1,0 |
1,7 |
|
|
Examination of living Persons |
11 1,1 |
9 0,8 |
3 0,2 |
23 0,7 |
_ |
2,5 |
|
Searching |
4 0,4 |
5 0,4 |
3 0,2 |
12 0,3 |
0,6 |
_ |
|
Exhumation |
4 0,4 |
2 0,2 |
5 0,4 |
11 0,3 |
0,6 |
|
|
TOTAL |
974 100 |
1132 100 |
1245 100 |
3351 100 |
|
|
|

Diagram 1. Number of forensic autopsies (n) and the average rate of participation (%) in crime scene inspection.
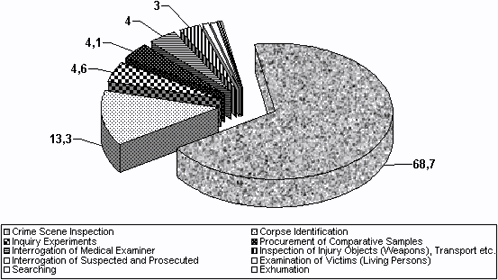
Diagram 2. The Structure of Inquests with participation of Medical Examiners in LR, 1998-2000 (%).
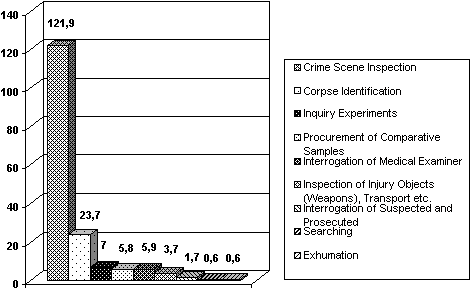
Diagram 3. The number of inquests with participation of medical examiners per 1.000 forensic autopsies (LR, 1998-2000).
Index of authors
Aihara, H. 63, 81
Aihara, M. 63, 81
Behnsen, S. 120
Berzins, U. 104
Bockholdt, B. 92
Bojarun, R. 173
Chvatovic, G. 156, 160
Dezhinova, T. 55
Franzmann, M. 107, 116
Ganulevics, Z. 72
Garmus, A. 173
Grass, H. 120
Grauss, G. 72
Grinenko, A. 21
Hansen, S. H. 107, 116
Hirvonen, J. 165
Hougen, H. P. 116
Huumonen, S. 165
Jakubėnienė, M. 179
Jegorova, N. 59
Kaju, S. 51
Kase, H. 77
Khodasevitch, L. 136, 141
Khodasevitch, T. 128
Kimont, H.-G. 120
Kortelainen, S. 165
Kringsholm, B. 116, 145
Kõiveer, A. 187
Kõlves, K. 15
Käferstein, H. 120
Kurganova I. 190
Lepik, D. 26
Loban I. 190
Lutere, Z. 45,
Mayatskaya, M. 149
Mäkivuoti, M. 165
Nēliuss, U. 51
Pallo, H. 111
Pankova, M. 9
Popov, V. 21
Putaala, J. 165
Raatiniemi, L. 165
Rotbergs, J. 141
Rybalko, J. 59
Safrai, A. 43
Schneider, V. 92
Sitienė, R. 179
Skidenko, N. 9
Smolyanitskaya, A. 149
Smolyanitsky, A. 149
Staak, M. 120
Steentoft, A. 145
Striks, E. 51
Särkioja, T. 165,
Zaslavsky, G. 21, 149
Tasa, G. 187
Teteris, O. 32, 97
Truschus, V. 45
Tuusov, J. 77
Vabels, G. 9
Vaitkevičius, E. 179
Vamze, J. 45
Vassiljev, V. 26, 187
Visciulyte, L. 59
Volgram, J. 128, 132, 141
Volksone, V. 104
Väli, M. 15, 77
Värnik, A. 15
Yushkovsky, V. 21
|